Transforming AI Training Data into Natural Language... Decoding the AI Black Box
- Input
- 2025-12-28 08:00:00
- Updated
- 2025-12-28 08:00:00
The Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) announced on the 28th that Professor Taehwan Kim and his team at the Graduate School of Artificial Intelligence have proposed a new training methodology for artificial intelligence (AI). By converting AI training data into human-understandable natural language, this approach aims to explain the AI black box.
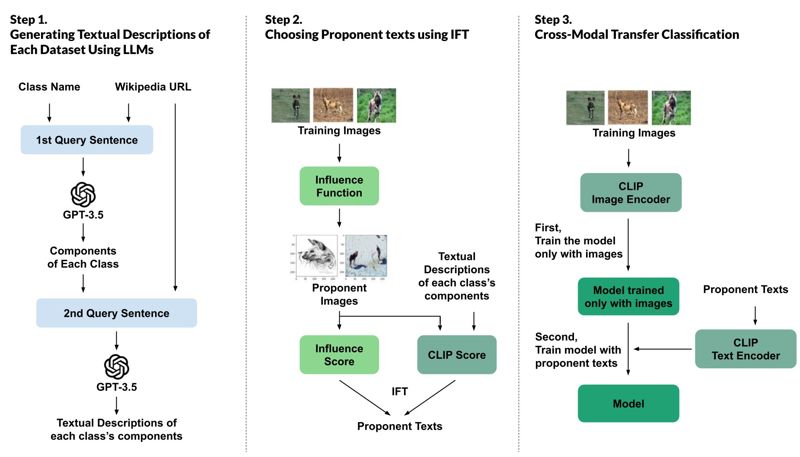
Previous research on Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) has mainly focused on post-hoc analysis of a trained model’s internal operations or prediction outcomes. In contrast, the research team turned their attention to the source of AI learning—data itself. By articulating the characteristics of the data through explanatory statements and analyzing them, they sought to clarify the model’s decision-making process.
The team first used LLMs such as ChatGPT to generate multiple sentences describing the features of objects in photographs. To ensure high-quality explanations without hallucinations, they also referenced external knowledge sources like online encyclopedias.
To verify whether these influential explanations actually enhance model performance, the researchers designed a separate benchmark experiment. They provided the model with high-impact explanations during training and conducted cross-modal transfer experiments, performing classification tasks on new datasets.
The results showed that using highly influential explanations led to consistently better performance than traditional methods. This validates that the explanations actually utilized by the model during training make a meaningful contribution to its performance.
Professor Taehwan Kim stated, “The approach proposed in this study, where AI explains the data it learns, could fundamentally reveal the complex decision-making process of deep learning. This will serve as a foundation for transparent understanding of black-box AI systems in the future.”
The research was accepted as a full paper at Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), a leading international conference in the field of NLP. This year’s EMNLP was held in Suzhou, China, from November 5 to 9.
jiany@fnnews.com Yeon Ji-an Reporter