"A Lump on His Knee"—What Was Found Inside a Man in His 20s? [Health Talk]
- Input
- 2025-11-21 05:40:36
- Updated
- 2025-11-21 05:40:36
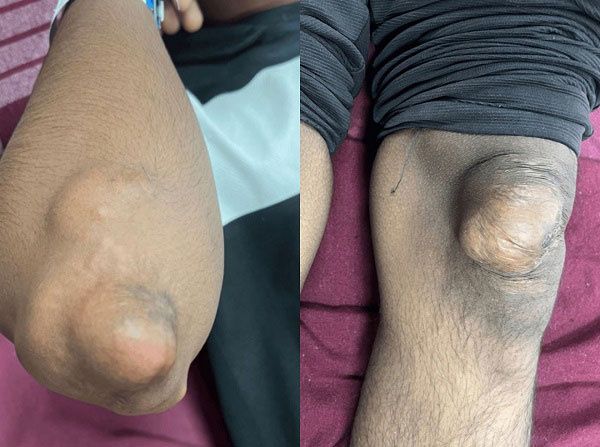
[Financial News] A rare case has been documented in India where a man in his 20s, suffering from familial hypercholesterolemia (FH), developed massive xanthomas throughout his body.
According to orthopedic staff at Manipal Hospital Bangalore, a 20-year-old man recently visited the hospital with multiple tumors on both elbows, knees, and buttocks. Tests revealed that the tumor on his elbow measured 6 cm by 4 cm, the one on his knee was 7 cm by 3 cm, and the lesion on his buttock was 9 cm by 4 cm, among other varying sizes.
As the tumors grew, the patient experienced severe discomfort and pain. He explained, "The tumor on my buttock made it difficult to sit, and it also caused hygiene issues. Wearing short sleeves and shorts became a challenge."
Given his history of familial hypercholesterolemia, the medical team diagnosed him with xanthoma, a condition characterized by yellowish lesions caused by abnormal cholesterol metabolism in the body. The patient subsequently underwent surgery to remove the tumors.
Xanthoma occurs when cholesterol accumulates beneath the skin. While it most commonly appears around the eyes and face, as in this case, it can also develop on other parts of the body such as the elbows or legs. The hallmark of xanthoma is flat or slightly raised yellowish lesions on the skin, usually without pain.
The main cause of xanthoma is abnormal blood cholesterol levels. It is more likely to occur in people with hyperlipidemia or hypercholesterolemia, and can also be influenced by diabetes, hypothyroidism, or liver disease. Genetic factors play a significant role, so those with a family history are at higher risk.
Although this condition does not typically cause pain or direct physical danger, it can serve as a warning sign of underlying health issues. High blood cholesterol can lead to fat buildup in the arteries, resulting in atherosclerosis. This systemic narrowing of the arteries increases the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), stroke, or cardiac arrest.
Experts therefore recommend that anyone diagnosed with xanthoma should have their blood lipid levels and overall health status evaluated.
This case was published in the medical journal Cureus on the 17th.
hsg@fnnews.com Han Seung-gon Reporter